As global supply chains adapt to shifting consumer expectations, labor shortages, and environmental pressures, one area undergoing rapid transformation is the warehouse. Long viewed as the engine room of logistics, warehouses are now at the forefront of innovation, propelled by advancements in robotics, AI, and sustainability practices.
Today’s most forward-thinking facilities are embracing a new paradigm: the smart warehouse. This concept goes beyond automating tasks. It integrates intelligent systems across physical and digital domains to boost efficiency, accuracy, and environmental responsibility. Here’s a look at the three central pillars shaping the future of warehousing: robotics and automation, digital solutions, and sustainability.
Robotics and automation: The foundation of smart warehousing
Smart warehousing starts with robotics and automation, which solve both efficiency and labor challenges. As outlined in the MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics report, The Warehouse of the Future (2024), robotics—from autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) to robotic picking arms—are becoming essential for boosting throughput and flexibility.
These technologies operate with high precision and minimal downtime, improving accuracy and speed while freeing up human workers for more value-added tasks.
A significant innovation in this space is the rise of collaborative robots (cobots). Unlike traditional industrial robots that work in isolation, cobots are designed to operate side-by-side with people. In warehouses, they assist with picking, lifting, or navigating complex paths—enhancing human capability while reducing physical strain.
Cobots offer flexibility, quick deployment, and adaptability, making them ideal in dynamic environments or where full automation isn't viable. When paired with proper workforce training, cobots create a human-machine partnership that drives both productivity and safety.
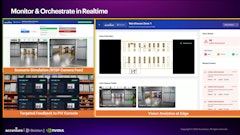
Digital solutions: Computer vision and digital twins
Physical automation is complemented by digital intelligence, particularly AI-integrated computer vision and digital twins.
Computer vision brings real-time visibility to warehouse operations. AI-powered cameras monitor inventory, identify misplacements, detect safety risks, and optimize workflows—reducing errors and improving speed, especially in high-volume facilities.
Digital twins take smart warehousing to the next level by creating live virtual models of the warehouse. This capability typically unfolds in three steps:
- Real-time visibility. Data from IoT devices, robotics, and WMS platforms flows into one system, offering a unified, real-time view of the facility—enabling faster, data-driven decisions.
- Operational optimization. With all data centralized, digital twins can pinpoint inefficiencies—like congestion or slow pick paths—and recommend adjustments to boost performance.
- Simulation and what-if scenarios. Leaders can safely test layout changes, automation investments, or seasonal shifts without disrupting real operations—using the digital twin as a sandbox for smarter planning.
This shift from reactive to predictive control helps organizations stay agile and proactive in an increasingly volatile supply chain landscape.
Sustainability: Making warehouses greener—and smarter
Modern warehousing must also address sustainability, not as a bonus, but as a strategic imperative.
Facilities are adopting energy-efficient systems, including smart lighting, motion controls, and HVAC automation. Many are integrating renewable energy sources like rooftop solar, often paired with on-site battery storage to reduce grid reliance.
Sustainability is also data-driven. AI-powered forecasting helps prevent overstock and waste, while computer vision minimizes packaging errors. Digital twins allow teams to simulate energy use or emissions before implementing new workflows—aligning operational goals with environmental targets.
Sustainability and technology should not be seen as competing forces, but rather mutually reinforcing pillars of future-ready logistics.
The integrated future: People, processes, and platforms
Smart warehousing is not just about technology—it’s about connecting people, processes, and platforms. A well-trained workforce is key to working effectively alongside machines. Interoperable systems allow seamless data exchange between WMS, robotics, and energy management tools.
The result is a facility that is not just faster—but resilient, adaptable, and sustainable.
Final thoughts
As supply chains grow more complex, warehouses are evolving from cost centers into strategic value hubs. Robotics and automation bring speed. Digital tools provide intelligence. Sustainability ensures long-term viability.
Together, they form the blueprint for the smart warehouse of the future.