=
Today’s organizations are seeing the advantages of incorporating key functions and geographies into a global business services (GBS) delivery model. According to KPMG research, key drivers for GBS adoption include the ability to support growth in emerging markets and improve operational efficiency while mitigating overall business risk.
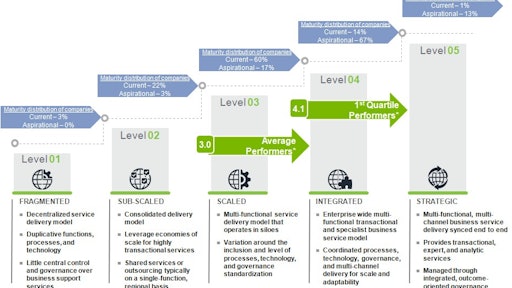
Many organizations began their journey toward GBS maturity by supporting traditional back-office functions such as finance, accounting, human resources (HR), information technology (IT) and procurement. As the GBS group became more mature, additional functions were often added, such as sales, marketing, research and development, design, legal and real estate.
As described in the chart above, the first and second maturity levels of GBS enable an organization to move from fragmented and siloed services to a more consolidated model that reduces redundancy, and improves governance and economies of scale for highly transactional services such as payroll. The focus is on increased efficiency through standardization, simplification, scaling, labor arbitrage, transparency and control. From Level 3 to 5, the focus is more on end-to-end optimization, agility, analytics, insights, innovation, governance and compliance.
However, moving to higher levels of GBS maturity is a challenge for many organizations, often because they lack a common service management infrastructure to support the strategic integration of business services across functions.
A Function-Agnostic Approach for Service Management
Enterprise service management (ESM) can be a key enabler for increased GBS maturity. ESM is a framework designed to provide a function-agnostic approach for service management. Multiple services and service channels can be designed, sourced, delivered and managed within a common framework, thereby overcoming traditional divisions and silos among different functions, as well as business units, technology platforms and governance principles.
ESM builds on proven service management methodologies such as the information technology infrastructure library (ITIL) for IT services that were developed and refined over decades. Properly implemented, ESM can mitigate inefficiencies, inconsistencies and redundancies in business services, helping to improve service value, increase agility, enhance consumer experiences and support sustainable business performance across the enterprise.
Supporting a Consistent, Enhanced Consumer Experience
One of the most important benefits of ESM principles, workflows, and enabling technologies is the ability to simplify and enhance the consumer experience while still maintaining process discipline and governance.
As companies strive for simplified, streamlined, cross-function/-multi function service design, having a common service management approach used by each function is critical. Services that require specific sequencing and specific approvals across groups can be significantly improved. For example, onboarding a new employee usually involves services from HR, payroll, IT and other functions. ESM supports a consistent, integrated approach for delivering these services, reducing the effort required for onboarding and helping the employee to become productive more quickly. ESM can also be used to develop intuitive, interactive self-service portals for employees that can reduce administrative costs while improving the speed of services. These portals also provide a consistent look and feel for the interface between employees and the organization, whether at a desk computer, kiosk or mobile device.
Equally important, ESM principles can help managers within each function to think more in terms of their workplace consumers by tailoring services to specific workgroups and new service demands. On the transaction side, services can be optimized and bundled so that wait times are reduced. Frequently, this approach of tailoring services to well-defined workgroup needs can also eliminate the consumption of un-needed, low-value capabilities. In addition, research shows that improved service quality can increase employee engagement and retention.
Fully Leveraging the Benefits of GBS
Many organizations reached a plateau in their GBS adoption levels as they try to manage a growing number and volume of services, increased demands by consumers, disruptive technologies, expanding regulations, different regional service needs and the integration of new acquisitions. Based on a practical, consistent approach to service management, ESM can help deliver multi-function, synchronized, end-to-end business solutions in full alignment with the long-term goals of the organization.
























